ophthafutur®
sf6 | c2f6 | c3f8
ophthafutur® sf6 | c2f6 | c3f8 are fluorinated gases used to tamponade the retina, offering an innovative solution for single use application.
- High purity
- Adjustable gas concentration
- Environmentally conscious system
- Sterile
- 24 months shelf life

What are fluorinated gases?
Fluorinated gases (F-gases) are a family of synthetic gases used in ophthalmic surgery since the 1970s.
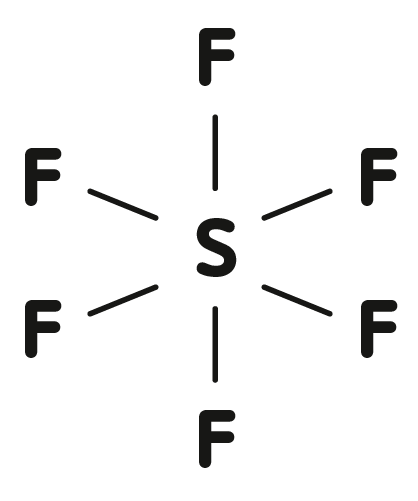
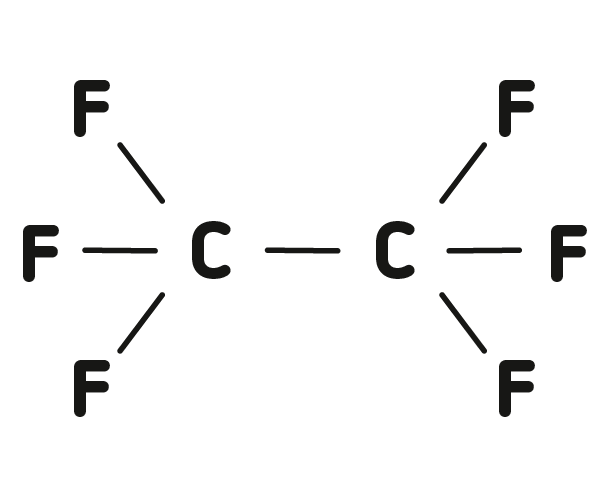
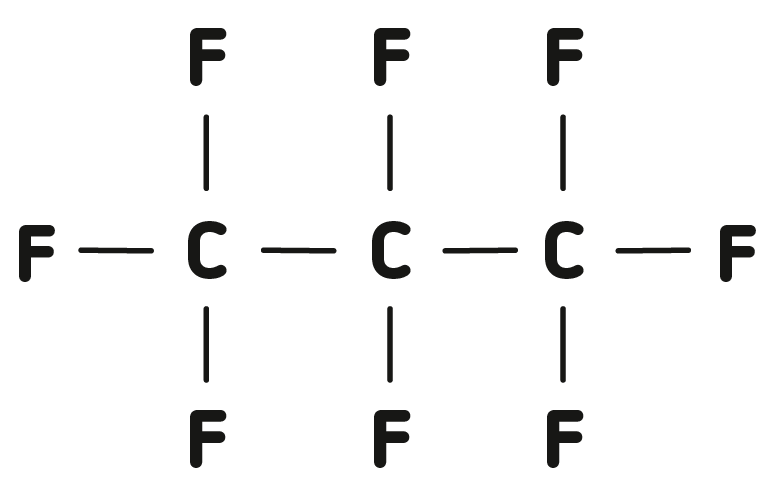
Fluorinated gases are chemically and physiologically inert, colorless and odorless gases intended as tamponade after operative treatment of severe retinal detachment.
The Challenge
Carbon footprint
The climate change is a global threat in the 21st century: the health care sector, whose mission is to heal and not “to do harm”, has a significant climate footprint and makes a major contribution to the climate crisis.
In 1997 The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, known as the Kyoto Protocol, identified seven greenhouse gases, including the three main gases used in ophthalmic surgery.

For example, the specific warming potential of SF6 is 23,900 times higher compared to CO2!
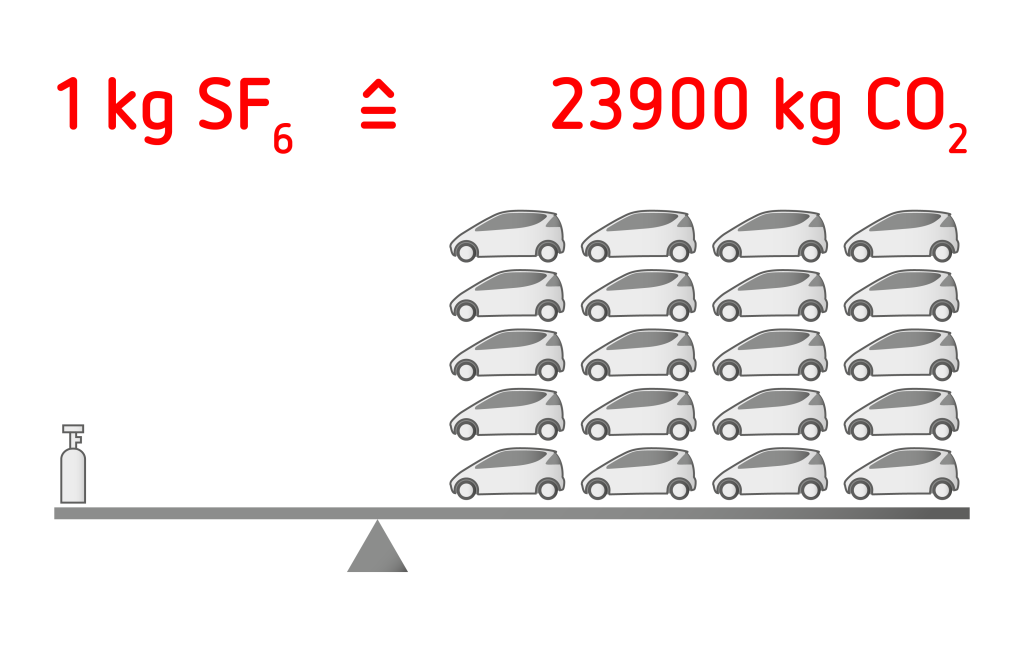
As a result, the use of F-gases such as SF6 are controlled by the the European Commission with the aim of reducing their use by two-thirds by 2030 (compared to 2014). Therefore, the use of F-gases and, above all, the associated emissions must be minimized.
Scientist and surgeons of the ophthalmic sector understand the criticality and different studies have been devoted to establishing the specific contribution of the potent greenhouse gases used in vitreoretinal surgeries.
It has been demonstrated that their impact varies depending on the gas type and on the gas delivery system and it has also been shown that SF6 causes significantly higher carbon emissions compared to C2F6 and C3F8.
George Moussa et al.:The use of fluorinated gases and quantification of carbon emission for common vitreoretinal procedures, Eye volume 37, pages1405–1409 (2023)
Ophthalmologists, with their choices, have a role in making changes to mitigate the carbon footprint of ophthalmic surgery.
Laura Wakely: Sustainability in eyecare: Intraocular gases and the climate emergency, Eye News, August 4, 2021
Traditional ophthalmic gas supply are large cylinders and multi-dose canisters
With this type of containers gas is difficult to transfer in the exact required quantities, which can lead to unnecessary high and/or uncontrolled emissions. Generally, leakages can occur easily during the manufacturing process and during surgeries.
The Solution
A 360-degree approach to the emissions problem
The ultimate solution to prevent the environmental impact of ophthalmic F-gases is reducing their use by limiting their application to the only cases where they are really necessary.
Alternatives for gas usage in vitreoretinal surgeries could be represented by the application of air, weaker concentrations of C2F6 and C3F8 in selected cases to replace FS6 during vitrectomy, as well as by scleral buckling or pneumatic retinopexy procedures.
Boon Lin Teh, et al.: Reducing the use of fluorinated gases in vitreoretinal surgery, Eye (2023)
However, the studies demonstrating that air tamponade (AT) has an excellent safety profile in the management of RRD, also highlight that it can only be used in selected cases, and that further studies are required to determine the most environmentally-friendly intraocular endotamponade without compromising patient outcomes.
Boon Lin Teh, et al.: Reducing the use of fluorinated gases in vitreoretinal surgery, Eye (2023)
When considering the potent green-house effects of F-gases, it is important to keep in mind that major uncontrolled emissions may occur at all stages of the supply chain: starting from the raw material manufacturing, over the device manufacturing, to the application and handling of the device and, finally, to waste management.
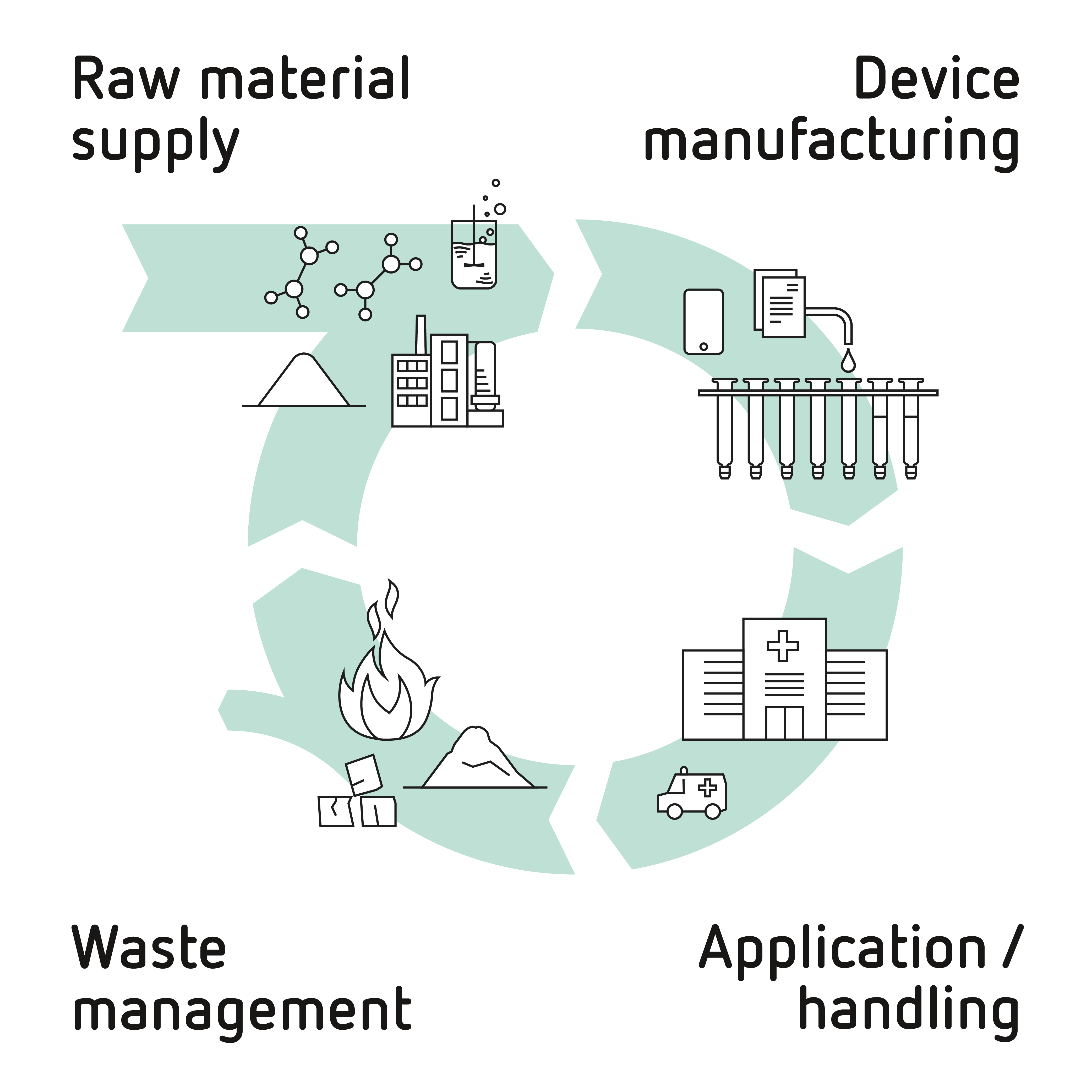
ophthafutur® F-gas solution is the result of extensive research and development activities supported by careful and environmentally conscious choices in all stages of the supply chain wherever the manufacturer can play a role:
- High quality raw materials are sourced from selected European companies fulfilling all requirements for emissions control as per the EU legislation to control F-gases
- A tailor-made manufacturing process minimizing emissions has been developed and implemented
- A practical, environmentally conscious delivery system is offered: the optimal amount of gas needed is provided in a non-pressurized glass container
- Waste management recommendations to turn left-overs into non-environmentally impacting components are provided

Usability
ophthafutur® gas is supplied in gas-tight borosilicate glass containers. The system includes a preassembled sterile plastic syringe to prepare the gas mixture and a small gauge needle to facilitate injection. A patient information card and a patient wristband are also provided.
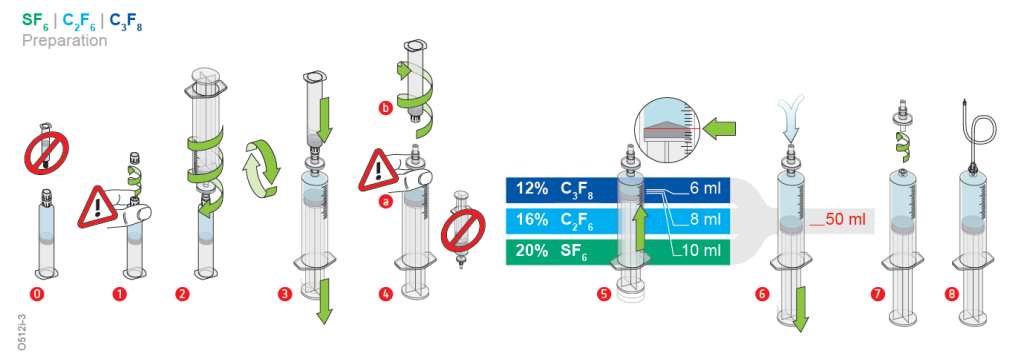
ophthafutur® gas system and preparation
Handling of ophthafutur gases video
For further in-depth information please contact your local distributor.




